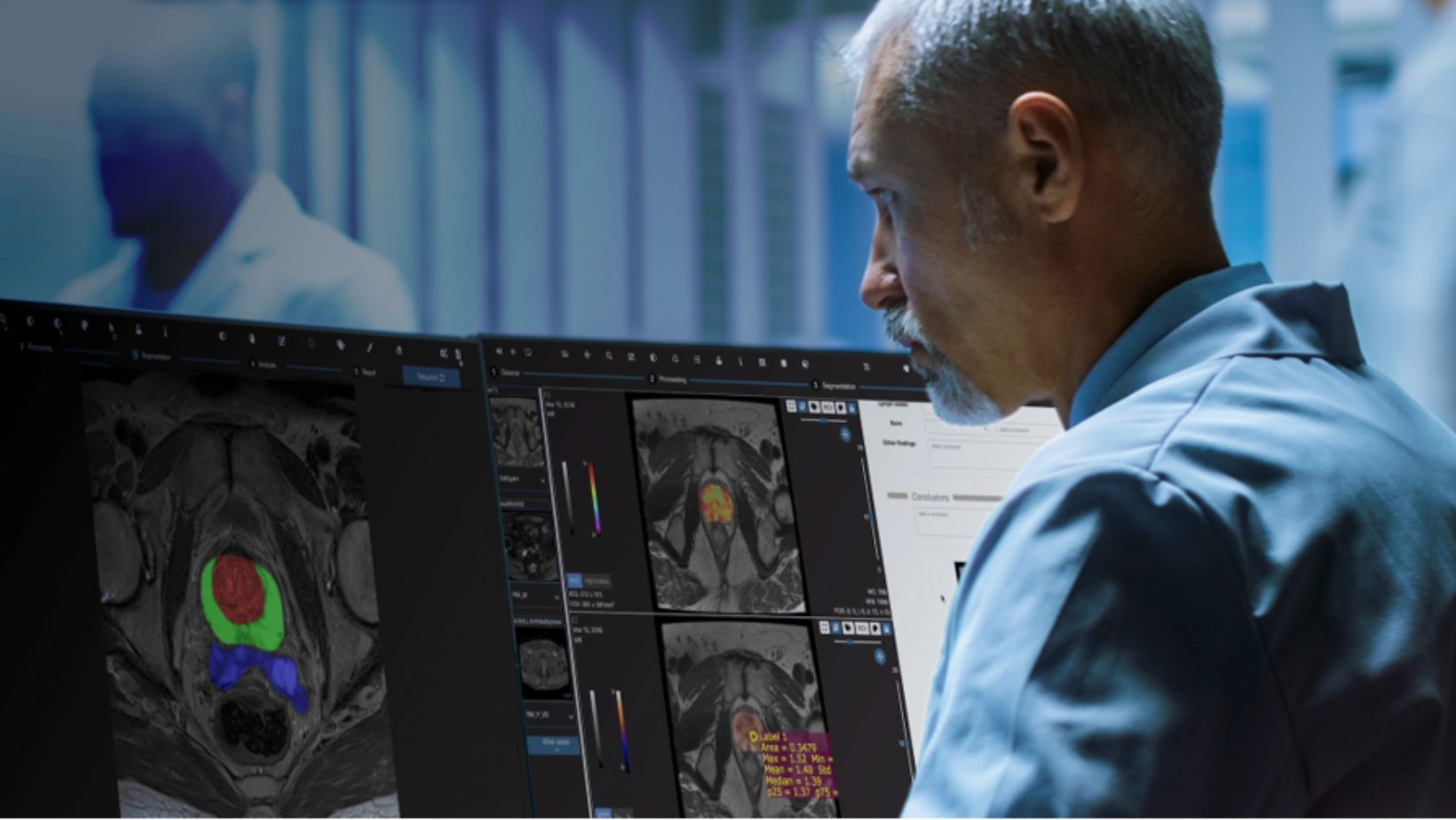
The rapid growth in medical imaging and the digitization of the process have created large repositories that contain valuable insights for improving patient outcomes. Yet, the biopharma industry’s ability to extract these insights has been limited by its lack of tools for transforming imaging data into actionable predictions. Quibim is addressing this critical limitation with its cloud-based tissue-agnostic platform for extracting key radiomics drivers from the world’s largest imaging-data registries.
Quibim has developed QP-Discovery, a platform that handles, indexes, stores, and harmonizes imaging data (Fig. 1). By standardizing image quality, the platform minimizes variability in the signal, contrast, and noise across equipment vendors. Quibim has paired its platform with a tool, QP-Link, to link imaging data with electronic health-record information and other multi-omics techniques.
QP-Link is the bridge between local picture-archiving and communication systems (PACS) and the Quibim cloud. The tool de-identifies medical images, removing patient identifiable data, and shares the images with Quibim’s analysis tools. Once the analysis is complete, QP-Link automatically sends the results back to the hospital PACS. Since Quibim’s commercial launch in 2021, more than 125 sites worldwide have begun using the platforms.
These platforms set Quibim apart from other companies that are applying artificial intelligence (AI) to medical imaging. Most companies are trying to improve radiology workflows. Quibim, in contrast, is focused on creating medical devices that bring its breakthroughs to healthcare providers. The idea is to design tools that unlock imaging data to improve patient outcomes.
Drug developers, including Johnson & Johnson’s Janssen Pharmaceuticals, have recognized the potential of Quibim’s capabilities. Working with a top-tier biopharma company, Quibim has developed an AI-based model to predict treatment response to immune-checkpoint inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer using baseline chest computed tomography (CT) scans. This model could enable the identification of those patients who are most likely to respond to treatment and is proof of Quibim’s ambition.
“We like to work with biopharma to solve big challenges, such as predicting how patients will respond to immunotherapy,” said Quibim CEO Ángel Alberich-Bayarri. “We are using data to generate new knowledge and new biomarker panels, both in partnership with biopharma companies and through our own studies. Evidence generation is central to our model.”
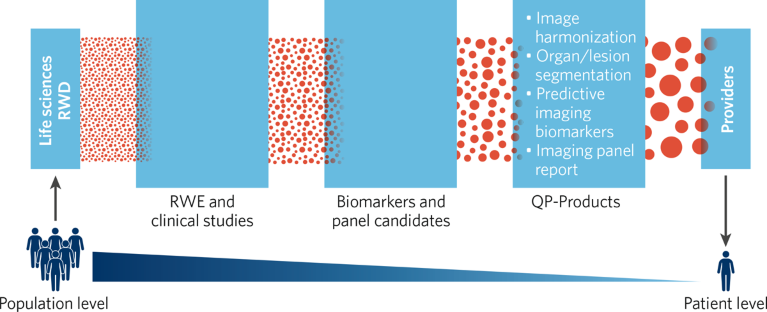
Fig. 1 | From population to patient level. RWD, real-world data; RWE, real-world evidence.
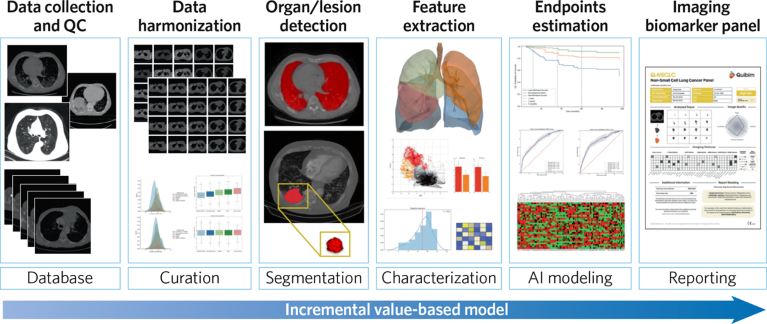
Quibim’s successes are built on three elements: data, technology, and partnerships. The company has unique attributes in each of these areas, which are ushering in a radiomics-enabled era of precision health that will be defined by the ability to use predictive modeling to uncover patterns and characteristics in medical images to improve outcomes (Fig. 2).
Data: building biobanks of health insights
Data are the bedrock of Quibim’s operations. The company is gathering as many datasets as possible covering images, clinical information, and patient outcomes, and is using these resources to generate new knowledge and imaging biomarkers. Access to appropriate data for training, testing, and evaluation of AI-based models is a key limitation to the field, which Quibim is fixing in collaboration with its partners.
The quantity of data is important, with larger volumes leading to additional, more robust insights, but this is far from the only metric that matters. Data quality is at least as important. When targeting subsets of patients, such as those with specific tumor profiles, there will always be major constraints on the amount of data available; however, data quality can compensate for quantity.
Recognizing that, Quibim focuses on accessing images with high-quality annotations that facilitate the feature-extraction process and ultimately enable the linking of imaging data to clinical outcomes. The focus on quantity and quality has led Quibim to commit to creating big international repositories of health-imaging data and to become involved in collaborative initiatives with different European countries. Through these initiatives, Quibim intends to foster the creation of European Union (EU)-wide structured repositories for health-imaging data as an open source for AI experimentation and for use by healthcare professionals, researchers, and innovators worldwide.
“We are involved in the best academic research projects related to cancer imaging,” Alberich-Bayarri said. “Quibim is the backbone platform for the biggest projects in cancer imaging in Europe. We can learn a lot from these data repositories, mainly across the most relevant indications: lung, prostate, breast, colorectal, and pediatric cancers.”
Chaimeleon and ProCancer-I, two EU-funded multidisciplinary and collaborative projects, are devoted to the creation of a cancer imaging repository, facilitating access to large, high-quality, anonymized datasets.
Quibim’s focus on data quality and quantity is matched by its commitment to data security by design. Holding certifications for the International Organization for Standardization and International Electrotechnical Commission (ISO/IEC) standard 27001, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) compliance, the company uses Microsoft Azure’s secure cloud platform for unlimited data storage. Information is encrypted during storage, transfer, and at the file leve