Βy Simone Mazzetti [Candiolo Cancer Institute, Torino-Italy]
Acquisition of high-quality magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) examinations is essential for the accurate detection and characterization of prostate cancer, as poor image quality can obscure lesions and undermine diagnostic confidence. The Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) guidelines establish standardized technical parameters to ensure optimal prostate MRI acquisition, while the Prostate Imaging Quality (PI-QUAL) scoring system provides a structured method to evaluate whether images meet the necessary quality standards for reliable clinical interpretation. Ensuring MRI examinations comply with both PI-RADS and PI-QUAL criteria is also important for artificial intelligence (AI) applications, since the performance and generalizability of algorithms depend on the consistency and quality of input data.
Training AI algorithms on MRI data that meet the guidelines helps ensure that the models learn from diagnostically valid examples, reducing the risk of bias introduced by suboptimal or artifact-laden images. Furthermore, incorporating PI-QUAL information into training datasets allows developers to stratify model performance based on image quality, identify failure points, and potentially build quality-aware AI systems capable of flagging poor-quality inputs in real-world settings.
As part of the EU-funded ProCancer-I project, we conducted a quality assessment of a subset of the ProstateNET dataset. A total of 850 MRI examinations were distributed among 13 readers from 10 Clinical Partners of the Consortium. Each MRI was independently assessed by two readers and, in case of disagreement, a third reader served as adjudicator. The study was conducted on the grand-challenge.org platform (Radboud University Medical Center), where the three MRI series (axial T2-weighted, DWI and ADC) and a set of guiding questions for radiologists were provided.
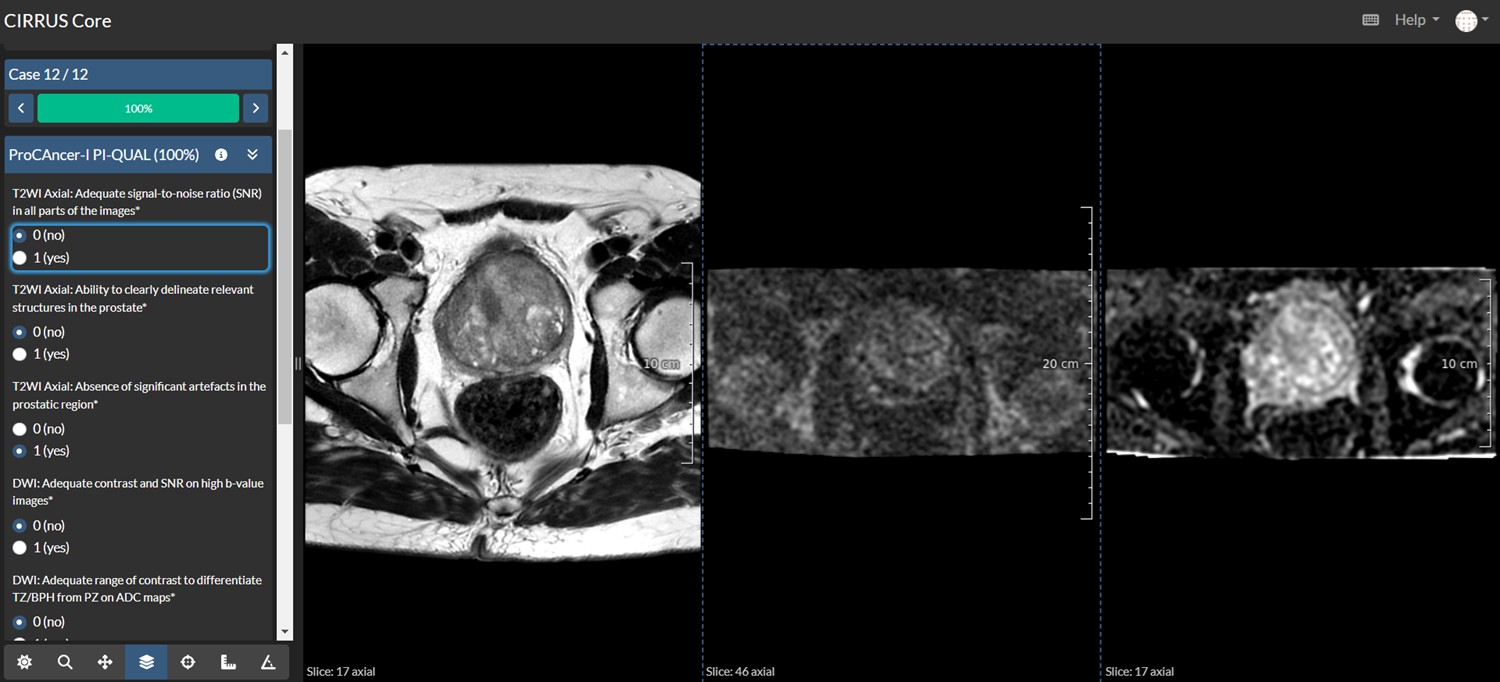
Example of the grand-challenge platform where the image quality assessment was conducted
At the end of the assessment, approximately 20% of the evaluated MRI examinations from ProstateNET were deemed to be of poor quality by the radiologists. Multivariate analysis revealed that the most frequent issues were an inadequate range of contrast on DWI and the presence of significant artefacts in the prostatic region.
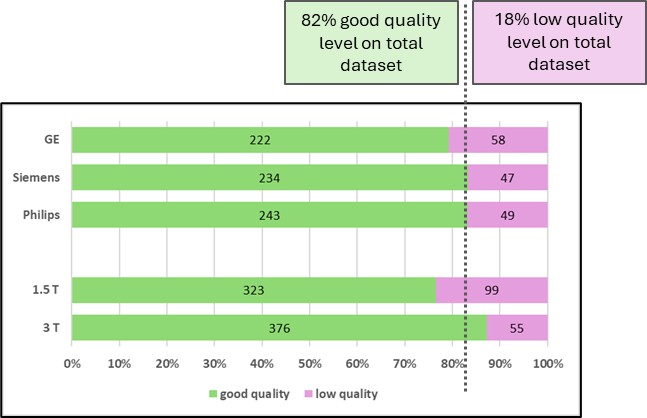
Distribution of good vs low quality MRI examinations, stratified by MRI vendor and magnetic field strength
This preliminary step lays the foundation for the development of an automated system to assess MRI quality, based on both technical parameters and visual assessment, to identify the cases for reliable AI applications.

